

Transformer模型出自论文“Attention is All You Need”,自其问世以来就迅速席卷了自然语言处理领域,并在各类主流任务上取得了新的突破,包括机器翻译、语言建模、序列标注和文本分类等。NiuTensor框架包含了Transformer的高效实现(NiuTensor/source/sample/transformer),本文以机器翻译任务为例,自顶向下对该结构进行分解,结合代码一步一步搭建完整的模型。
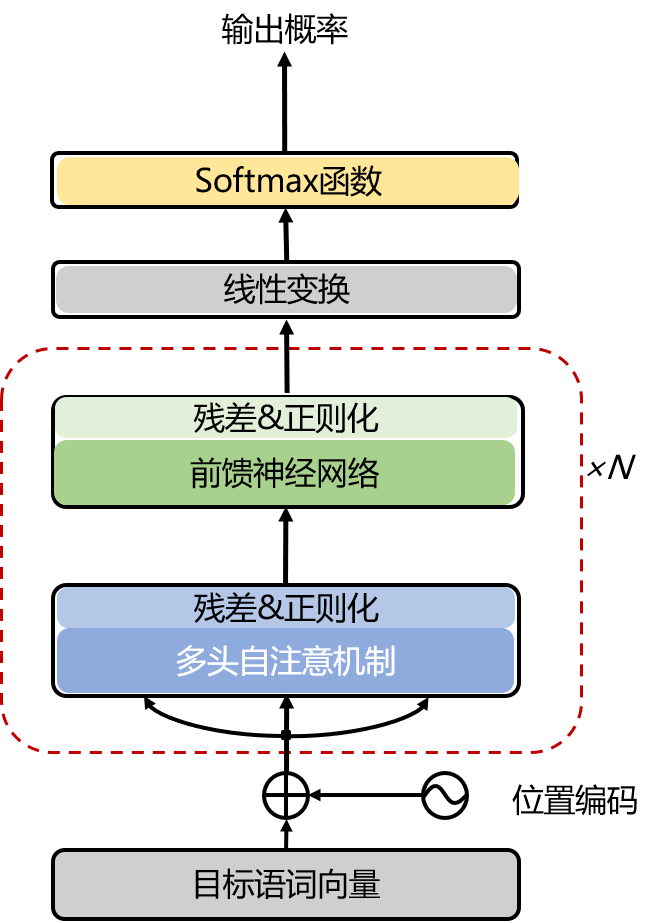
Transformer由Encoder和Decoder两部分组成,如图1所示,使用Encoder-Decoder模型进行机器翻译可以被概括为:输入源语通过模型计算输出目标语。
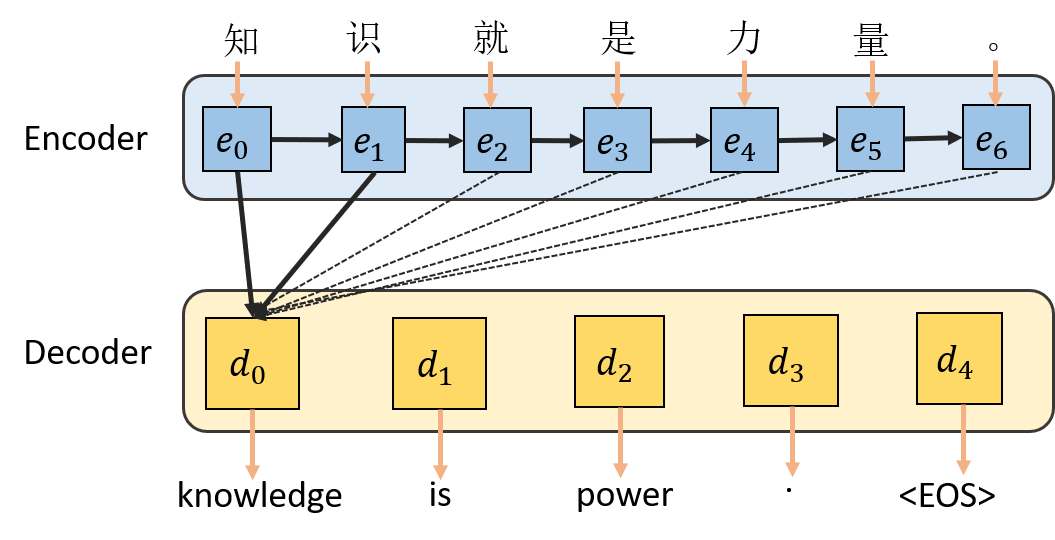
在Transformer中,encoder和decoder都由多层相同的结构堆叠而成,如图1.2所示。(6x代表将同样的结构堆叠6次)
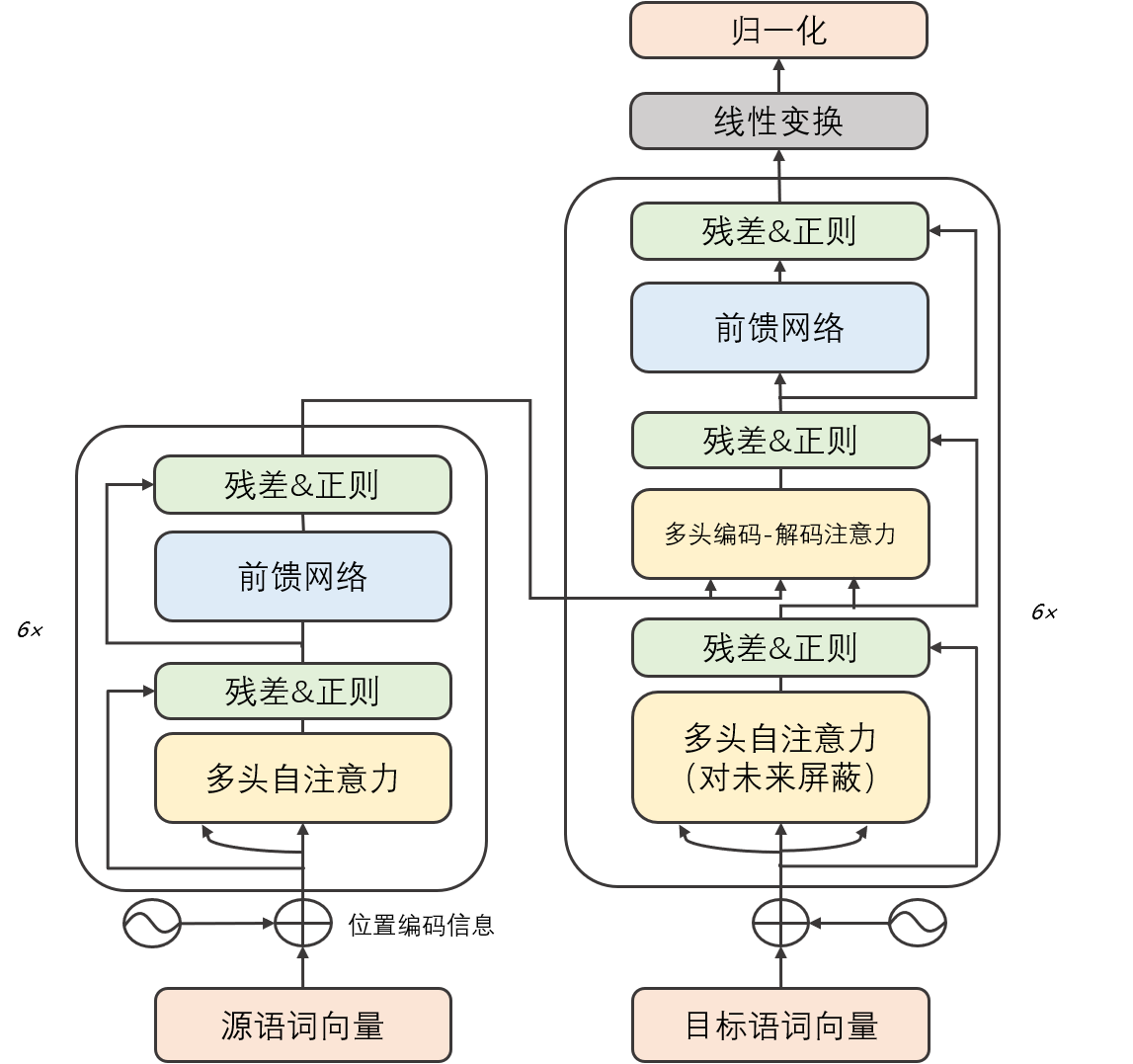
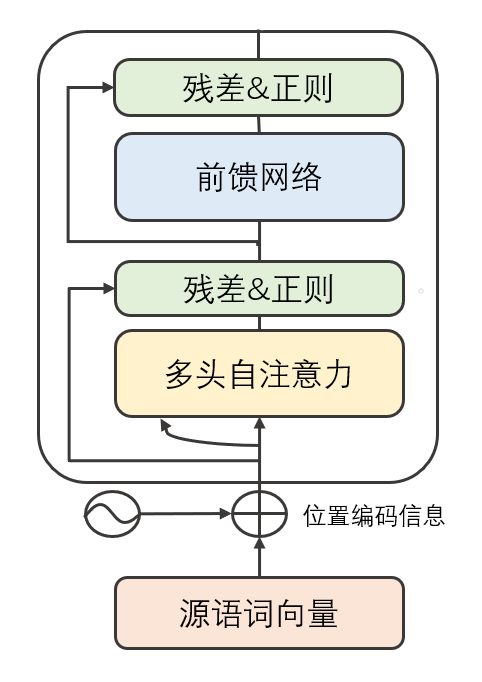
其中,每个encoder层又由两部分组成(先不讨论残差连接与正则化操作),包括一个前馈神经网络(FeedForward Neural Network,FNN)和一个自注意力层。(self-attention)encoder最底层的输入就是源语,先经过self-attention层,再传递到FNN层。
而decoder由三部分组成(同样先不讨论残差与正则),其self-attention最底层的输入是目标语,与encoder相比,它多出一个encoder-decoder attention层,其输入为encoder最后一层的输出。decoder顶层的输出依次经过线性变换和归一化得到目标词的概率。
上面的图片概述了Transformer模型的大致结构,现在从输入开始描述整个模型的计算流程。
首先是将输入的词汇转换为词向量,Transformer中的词向量由两部分相加而成,包括原始的词嵌入(Embeddings)和位置信息编码。固定的位置信息编码公式如下,其中代表当前词汇在整个输入句子中的相对位置,而代表了词向量维度,在原文中是512。(也可以替换为可学习的位置向量,即随模型训练而更新。)
Transformer位置信息编码在NiuTensor的实现如下:
/*
make positional embeddings (of size eSize * length)
>> eSize - embedding size
>> d - dimension size of the hidden layers
>> length - length of the sequence
*/
void T2TEmbedder::MakePosEmbedding(int eSize, int d, int length)
{
InitTensor2D(&posEmbeddingBase, length, eSize, X_FLOAT, devID);
float * data = new float[posEmbeddingBase.unitNum];
for(int pos = 0; pos < length; pos++){
float * dp = data + pos * eSize;
int channelSize = eSize / 2;
int offset = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < channelSize; i++){
dp[offset++] = (float)sin(pos/pow(10000.0F, 2.0F*i/(d - 2)));
}
for(int i = 0; i < channelSize; i++){
dp[offset++] = (float)cos(pos/pow(10000.0F, 2.0F*i/(d - 2)));
}
}
posEmbeddingBase.SetData(data, posEmbeddingBase.unitNum);
delete[] data;
}
接下来词向量被送入self-attention层,然后经过残差连接、层归一化操作,送入FNN层,再经过残差连接和层归一化操作,如图2.1所示。
Transformer中encoder部分对应的NiuTensor实现:
/*
make the encoding network
>> input - the input tensor of the encoder
>> mask - the mask that indicate each position is valid
>> maskEncDec - no use
>> isTraining - indicates whether the model is used for training
<< return - the output tensor of the encoder
*/
XTensor AttEncoder::Make(XTensor &input, XTensor &mask, XTensor &maskEncDec, bool isTraining)
{
XTensor x;
x = embedder.Make(input);
/* dropout */
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
x = Dropout(x, dropoutP);
for(int i = 0; i < nlayer; i++){
XTensor att;
XTensor ln;
XTensor fnn;
XTensor res;
/* self attention */
att = attentions[i].MakeBig(x, mask, isTraining);
/* dropout */
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
att = Dropout(att, dropoutP);
/* residual connection */
res = Sum(att, x);
/* layer normalization */
x = attLayerNorms[i].Make(res);
/* fnn */
fnn = fnns[i].Make(x, isTraining);
/* dropout */
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
fnn = Dropout(fnn, dropoutP);
/* residual connection */
res = Sum(fnn, x);
/* layer normalization */
x = fnnLayerNorms[i].Make(res);
}
x.SetName(ENCODING_NAME);
input.SetName(ENCODING_INPUT_NAME);
return x;
}
下面展示attention部分的计算方式,在NiuTensor的实现中包括两部分:
如图2.2所示,self-attention层中的,,是同一个东西,在encoder端最底层是源语词向量,在decoder端最底层是目标语的词向量。而encoder-decoder-attention层中的和是encoder端最顶层的输出,其中的在最底层是目标语的词向量。
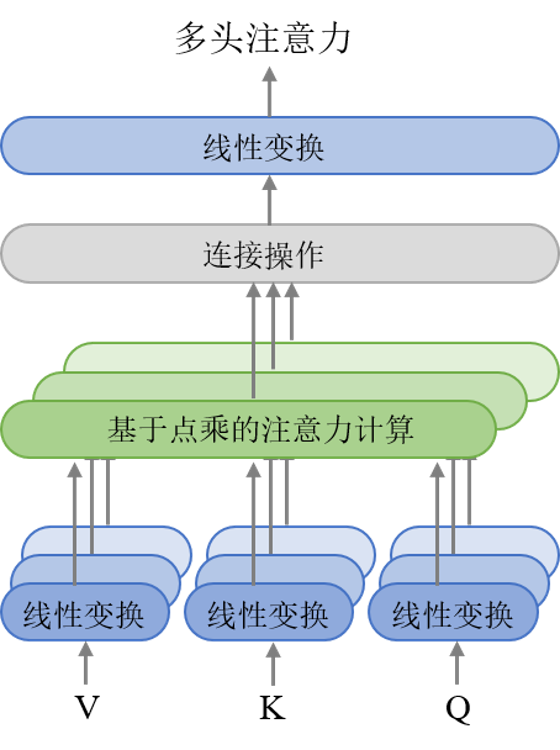
NiuTensor中对输入的,,进行线性变换的实现:
/*
make the network given a big tensor that keeps keys, queries and values
>> kqv - the big tensor
>> mask - as it is
>> isTraining - indicates whether the model is used for training
*/
XTensor T2TAttention::MakeBig(XTensor &kqv, XTensor &mask, bool isTraining)
{
XTensor k2;
XTensor q2;
XTensor v2;
XTensor kqv2;
TensorList split;
kqv2 = MMul(kqv, wbig);
int d1 = kqv2.GetDim(0);
int d2 = kqv2.GetDim(1);
int d3 = kqv2.GetDim(2) / 3;
InitTensor3D(&k2, d1, d2, d3, X_FLOAT, devID);
InitTensor3D(&q2, d1, d2, d3, X_FLOAT, devID);
InitTensor3D(&v2, d1, d2, d3, X_FLOAT, devID);
split.Add(&q2);
split.Add(&k2);
split.Add(&v2);
Split(kqv2, split, 2, 3);
return MakeAttention(k2, q2, v2, mask, isTraining);
}
在计算multihead attention时,按照如下公式:
其中,输入的,,(线性变换后的矩阵)先被等分为多个小矩阵(多头),原文中是8个头,多头分别进行attention计算,最后再拼接为大矩阵,经过线性变换再送到下一层,见图2.3。
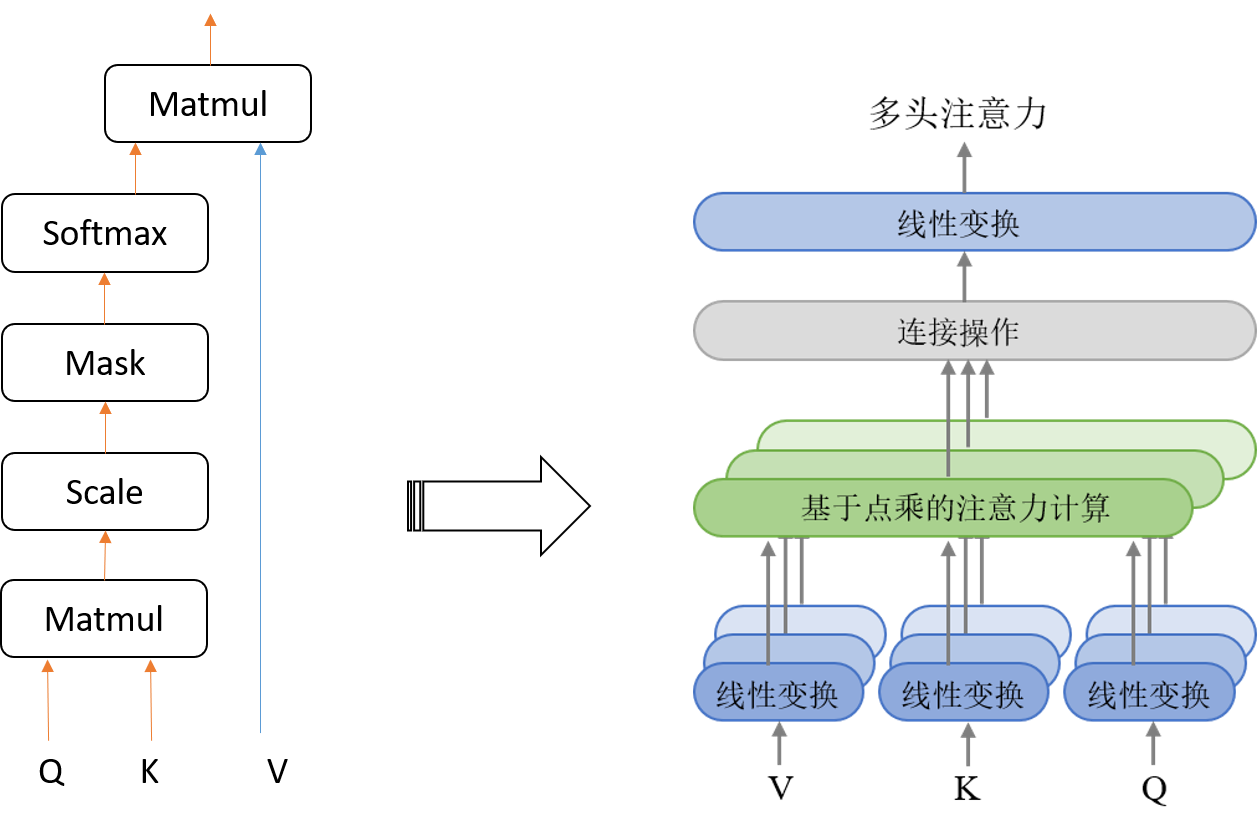
NiuTensor中attention操作的实现:
/*
make the attention network given keys, queries and values (after linear transformation)
>> k - keys. It might be of size B * L * H
where B = batch size, L = sequence length,
and H = vector size of each position
>> q - queries
>> v - values
>> mask - as it is
>> isTraining - indicates whether the model is used for training
*/
XTensor T2TAttention::MakeAttention(XTensor &k, XTensor &q, XTensor &v, XTensor &mask, bool isTraining)
{
XTensor kheads;
XTensor qheads;
XTensor vheads;
/* multi head */
kheads = Split(k, k.order - 1, nhead);
qheads = Split(q, q.order - 1, nhead);
vheads = Split(v, v.order - 1, nhead);
XTensor att;
XTensor dot;
XTensor scalar;
/* scalar = softmax(Q * K^T / sqrt(dk)) * V */
dot = BMMul(qheads, X_NOTRANS, kheads, X_TRANS);
if(isMasked)
dot = dot + mask;
dot = Linear(dot, 1.0F/(float)sqrt((float)dk/nhead));
scalar = Softmax(dot, -1);
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
scalar = Dropout(scalar, dropoutP);
att = BMMul(scalar, vheads);
/* concatenate the heads */
return MMul(Merge(att, att.order - 1), wa);
}
在得到attention权重之后,将其与该层的输入进行残差连接,之后进行层正则化操作,NiuTensor中层正则化的实现:
/*
make the network
for each layer representation x, we have
y =
>> input - the input tensor
>> return - layer normalization output
*/
XTensor T2TLN::Make(XTensor &input)
{
XTensor &x = input;
XTensor xn;
XTensor mean;
XTensor variance;
XTensor standard;
XTensor meanFilled;
XTensor standardFilled;
/* \mu = (sum_i x_i)/m */
mean = ReduceMean(x, x.order - 1);
/* \sigma = (sum_i (x_i - \mu)^2)/m */
variance = ReduceVariance(x, x.order - 1, mean);
/* standard = sqrt(variance) */
standard = Power(variance, 0.5F);
/* unsqueeze mean and standard deviation to fit them into
the same shape of x */
meanFilled = Unsqueeze(mean, x.order - 1, x.GetDim(-1));
standardFilled = Unsqueeze(standard, x.order - 1, x.GetDim(-1));
/* x' = (x - \mu)/standard */
xn = (x - meanFilled) / standardFilled;
/* result = x' * w + b */
return xn * w + b;
}
接下来是前馈神经网络层,即FNN,在NiuTensor中的实现如下:
/*
make the network
y = max(0, x * w1 + b1) * w2 + b2
>> input - the input tensor
>> return - the output tensor
*/
XTensor T2TFNN::Make(XTensor &input, bool isTraining)
{
XTensor t1;
/* t1 = max(0, x * w1 + b1) */
//t1 = Rectify(MMul(input, w1) + b1);
t1 = Rectify(MulAndShift(input, w1, b1));
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
t1 = Dropout(t1, dropoutP);
/* result = t1 * w2 + b2 */
//return MMul(t1, w2) + b2;
return MulAndShift(t1, w2, b2);
}
现在我们完成了整个encoder端的计算,而decoder端与之相比多出了计算encoder-decoder attention的部分,如图2.4所示。
encoder-decoder attention操作加在self-attention和FNN之间,同样具有,,三个输入,其中和均为encoder顶层的输出,而是decoder端的输入。在解码时,直到预测出结束符号才停止计算。最后,对decoder的输出进行线性变换和softmax操作,即可得到词表中每个目标词汇的概率。
NiuTensor中对应decoder部分的实现如下:
/*
make the decoding network
>> inputDec - the input tensor of the decoder
>> outputEnc - the output tensor of the encoder
>> mask - mask that indicates which position is valid
>> maskEncDec - mask for the encoder-decoder attention
>> isTraining - indicates whether the model is used for training
<< return - the output tensor of the encoder
*/
XTensor AttDecoder::Make(XTensor &inputDec, XTensor &outputEnc, XTensor &mask, XTensor &maskEncDec, bool isTraining)
{
XTensor x;
x = embedder.Make(inputDec);
/* dropout */
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
x = Dropout(x, dropoutP);
for(int i = 0; i < nlayer; i++){
XTensor att;
XTensor ende;
XTensor ln;
XTensor fnn;
XTensor res;
/******************/
/* self attention */
att = attentions[i].MakeBig(x, mask, isTraining);
/* dropout */
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
att = Dropout(att, dropoutP);
/* residual connection */
res = Sum(att, x);
/* layer normalization */
x = attLayerNorms[i].Make(res);
/*****************************/
/* encoder-decoder attention */
ende = attentionsEnde[i].Make(outputEnc, x, outputEnc, maskEncDec, isTraining);
/* dropout */
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
ende = Dropout(ende, dropoutP);
/* residual connection */
res = Sum(ende, x);
/* layer normalization */
x = attEndeLayerNorms[i].Make(res);
/*******/
/* fnn */
fnn = fnns[i].Make(x, isTraining);
/* dropout */
if(isTraining && dropoutP > 0)
fnn = Dropout(fnn, dropoutP);
/* residual connection */
res = Sum(fnn, x);
/* layer normalization */
x = fnnLayerNorms[i].Make(res);
}
x.SetName(DECODING_NAME);
return x;
}
最后附上NiuTensor中的完整的Transformer机器翻译模型实现:
/*
make the network for machine translation (with the output softmax layer)
>> inputEnc - input tensor of the encoder
>> inputDec - input tensor of the decoder
>> output - output tensor (distribution)
>> paddingEnc - padding of the sequences (on the encoder side)
>> paddingDec - padding of the sequences (on the decoder side)
>> isTraining - indicates whether the model is for training
*/
void T2TModel::MakeMT(XTensor &inputEnc, XTensor &inputDec, XTensor &output, XTensor &paddingEnc, XTensor &paddingDec, bool isTraining)
{
XTensor encoding;
XTensor decoding;
XTensor maskEnc;
XTensor maskDec;
XTensor maskEncDec;
/* encoder mask */
MakeMTMaskEnc(inputEnc, paddingEnc, maskEnc);
/* decoder mask */
MakeMTMaskDec(inputEnc, inputDec, paddingEnc, paddingDec, maskDec, maskEncDec);
encoding = MakeEncoder(inputEnc, maskEnc, isTraining);
decoding = MakeDecoder(inputDec, encoding, maskDec, maskEncDec, isTraining);
outputLayer->Make(decoding, output);
}